First Arabic Alphabet Letter, Get 1 to 28 Arabic Letters Order
Are you searching for the 1st letter of the Arabic alphabet? Get the answer with the photo, not only this, you will get the complete order here.
The first letter of the Arabic alphabet is ‘alif.’ This letter stands for the sound ‘a’ in English. The letter consists of a vertical line and a dot above it.
Table Description -> A – Serial Number, B – Isolated Form, C – Trans-literation, D – Letter name, E – Letter Name In Arabic Script.
| A | B | C | D | E |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ا | ā | ʾalif | أَلِف |
The first Arabic alphabet letter, ‘alif, has been newly detailed in a new report. The letter should be pronounced as ‘a-lee-f’ and not ‘a-li-‘ef’. The letter was previously thought to be pronounced as ‘a-lee-f’ due to a mistranscription from the 9th century.
Get 1 to 28 Arabic Letters Order
There is no one definitive answer to the question of the mysterious origins of the first letter in the Arabic alphabet. Some scholars believe that it was derived from an ancient Phoenician letter, while others argue that it may have been derived from the Aramaic letter Aleph.
Still others claim that it was an entirely new invention. Whatever its origins may be, there is no doubt that the letter Alif has played a central role in the development of the Arabic alphabet and language.
The order of the Arabic letters goes from one to twenty-eight. This is due to the fact that there are twenty-eight letters in the Arabic alphabet. The letters are ordered according to their place in the alphabet, so the first letter is ا (أَلِف), and the last letter isي (يَاء).
Table Description -> A – Serial Number, B – Isolated Form, C – Trans-literation, D – Letter name, E – Letter Name In Arabic Script.
| A | B | C | D | E |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ا | ā | ʾalif | أَلِف |
| 2 | ب | b | bāʾ | بَاء |
| 3 | ت | t | tāʾ | تَاء |
| 4 | ث | th | thāʾ | ثَاء |
| 5 | ج | j | jīm | جِيم |
| 6 | ح | ḥ | ḥāʾ | حَاء |
| 7 | خ | kh | khāʾ | خَاء |
| 8 | د | d | dāl | دَال |
| 9 | ذ | dh | dhāl | ذَال |
| 10 | ر | r | rāʾ | رَاء |
| 11 | ز | z | zāy | زَاي |
| 12 | س | s | sīn | سِين |
| 13 | ش | sh | shīn | شِين |
| 14 | ص | ṣ | ṣād | صَاد |
| 15 | ض | ḍ | ḍād | ضَاد |
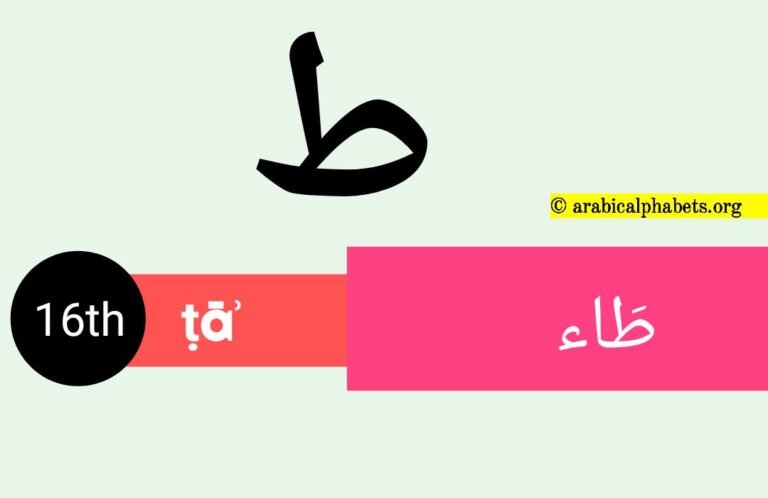
| 16 | ط | ṭ | ṭāʾ | طَاء |
| 17 | ظ | ẓ | ẓāʾ | ظَاء |
| 18 | ع | ʿ | ayn | عَيْن |
| 19 | غ | gh | ghayn | غَيْن |
| 20 | ف | f | fāʾ | فَاء |
| 21 | ق | q | qāf | قَاف |
| 22 | ك | k | kāf | كَاف |
| 23 | ل | l | lām | لاَم |
| 24 | م | m | mīm | مِيم |
| 25 | ن | n | nūn | نُون |
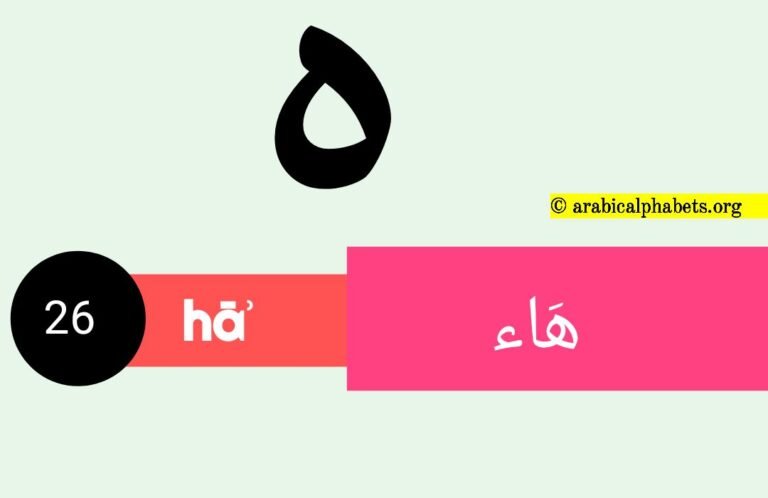
| 26 | ه | h | hāʾ | هَاء |
| 27 | و | w | wāw | وَاو |
| 28 | ي | y | yāʾ | يَاء |
In conclusion
It is evident that the Arabic alphabet is a rich and complex writing system that has been used for centuries. It is important to learn the basics of the Arabic alphabet in order to be able to read and write in this language.
There are many online resources available to help learners master the alphabet, and with a little practice, anyone can become proficient in this difficult but fascinating writing system.
In conclusion, the letter alif is the first letter of the Arabic alphabet and it stands for the sound a in English. It is a very important letter in the Arabic language, and it has many different uses. It is important to know how to pronounce this letter correctly, so that you can properly communicate in Arabic.